Careers
Projects & Resources
© 1990-2024. Universal Communications Group NZ Limited.
New Zealand NZBN 9429041139738
Site by Brisbane.
What is dark fibre and how can it benefit your business?
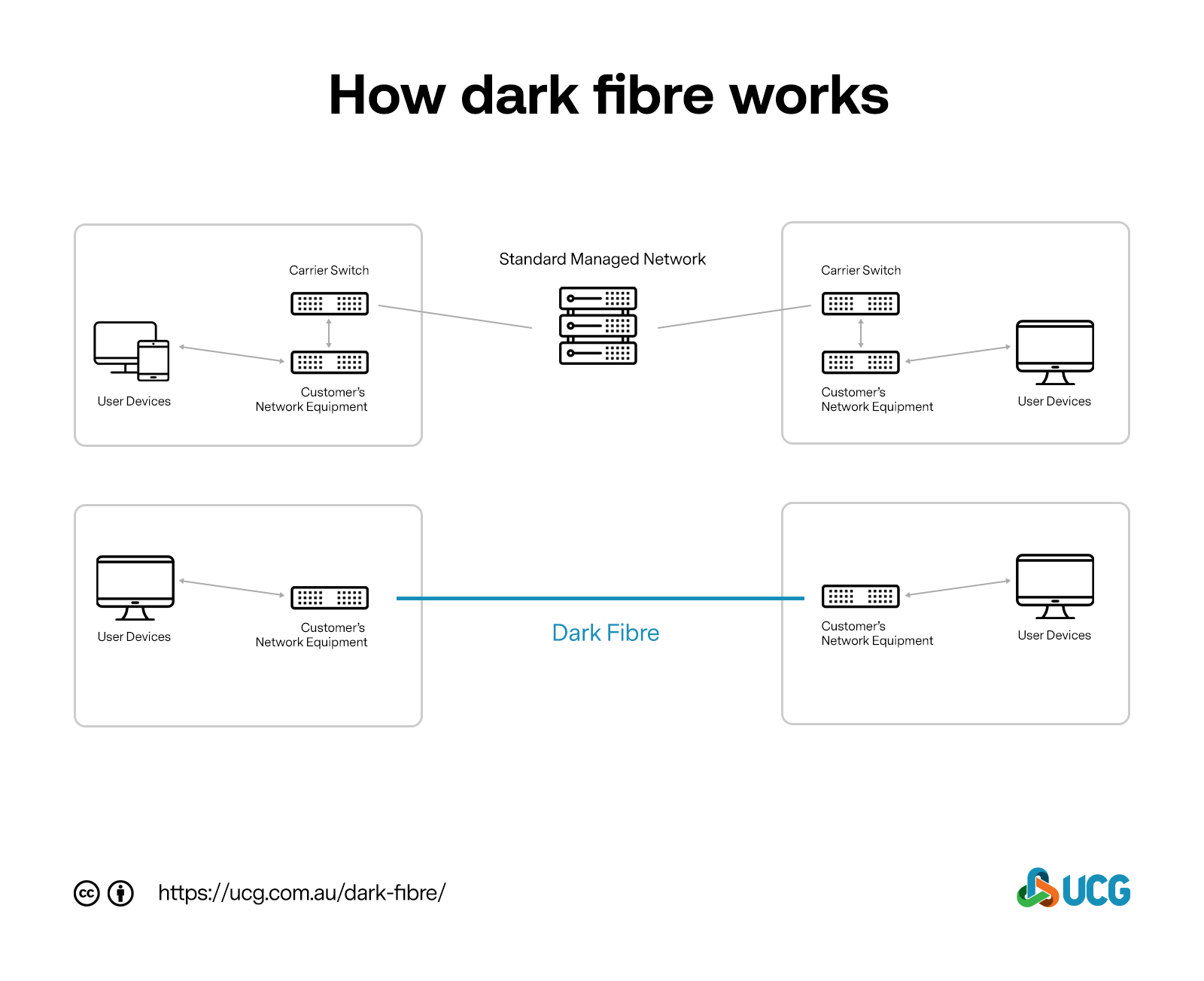
Dark fibre refers to optical fibre that has already been installed in the ground but is not in use. Also known as unlit fibre, dark fibre is available for rental or purchase from network service providers. Since most of the costs of installing cables in the ground involves the civil engineering work – obtaining permissions, planning, routing, then digging the trenches – it makes sense to plan and install significantly more fibre than is needed for the current demand. The outcome of this process is dark fibre, which is spare network fibre installed in the ground, ready to be leased to companies in the future.
Looking at major infrastructure projects like the NBN, we can see that modern fibre networks are labour and capital intensive. It makes the best economic sense that as much cable practically possible should be rolled out once the planning, mapping and digging has been done.
Once the cables have been laid, part of that network is activated (or “lit”) by the network service provider, whilst the remaining part of the network is “unlit”, as dark fibre. This dark fibre network is now ready for businesses to lease and direct their own optical fibre connections.
Dark fibre is generally available throughout New Zealand’s capital cities, and you may be connected in Brisbane, Sydney, Melbourne, Adelaide, Perth, Canberra, Hobart, and Darwin, among other major cities and metropolitan areas across New Zealand.
UCG are leading providers of telecommunications infrastructure across New Zealand. Talk to our team today about dark fibre at your premises.
On a typical active network, there are many customers using the same network simultaneously. With dark fibre, you may be the only customer, allowing you to have control over your IT capabilities and manage scale as you need it. Dark fibre has a range of uses, including connecting buildings, linking to data centres and creating direct connections between multiple sites you operate within a city. All these can also be achieved with typical managed networks, but dark fibre has a wide range of advantages over managed networks, including:
Undoubtedly, one of the most significant advantages of dark fibre is that it provides businesses with complete control and flexibility over their networks, equipment, and connection configurations. You have the ability to choose the type of transmission technology, protocols, and features that are appropriate for your company. This is possible because your business will not be sharing the service with anyone else.
This flexibility gives you scalability. A business that requires 1 Gbit/s today can upgrade to 10 Gbit/s and beyond tomorrow, without having to contact their ISP to request a speed increase. You can rapidly scale upwards to meet the evolving data needs of your business, with the only real limitation being the network equipment you decide to use.
Fibre has virtually no limit on the data it can transfer, which makes dark fibre an entirely future proof solution for your business. In today’s data hungry world, businesses need to be prepared for changes and increases in data use for new trends and technologies that appear in the market. By upgrading your network equipment as data demand increases, dark fibre allows you to scale up your network without having to dig and lay more fibre.
Modern fibre optic cable can hit up to 100Gpbs on a single wavelength and being the only operator using a dark fibre network you can optimise your setup for data or speed, by upgrading the equipment and transmission protocols. The entire bandwidth of the dark fibre network is yours, making it the perfect solution to future proof your business’ data needs.
Because you are the only user of the network, your data is more securely transferred than a traditional managed carrier service. Dark fibre is connected point-to-point, with cable maintained in ground, making it more secure and reliable than regular networks as you are not running through the carriers routing and switching equipment. Outages from damage to the cables or power supply are typically bypassed with dark fibre route diversity.
The fact that dark fibre is purely fibre infrastructure only means that when designing their own network, businesses can choose from a diverse range of technology to meet their needs. As long as businesses can source and install their chosen technology, whether it be DWDM or ethernet over MPLS, they can rely on dark fibre to provide the data capacity they need.
With dark fibre, you do not own the cables in the ground, you are only “operating” the network. This reduces your costs considerably by not being committed to the installation of the physical infrastructure. Dark fibre offers a cost-effective solution for businesses looking to expand their data needs as there is no investment in the fibre cables, only in network equipment and upgrades.
As cloud-based applications and services become more and more dominant, having a reliable and secure network can be vital to data reliant businesses. Dark fibre offers a solution to remove disruption to cloud-based services at a reduced cost. Since you have control over your equipment and transmission protocols, you have control over your costs. Businesses can explore many different solutions to find the best way to scale their network data requirements without being at the mercy of your service provider’s rates.

With the first fibre optic ocean cable buried under the Pacific Ocean in 1996, the world began the rapid expanse of fibre installation. The idea at the time, was that all telecommunications traffic, particularly data traffic, will continue to expand rapidly for the foreseeable future. While the dot-com bubble was in full swing during the late 1990’s, telephone companies around the world invested heavily in constructing fibre optic networks, each with the goal of cornering the telecommunications market by providing a network with sufficient capacity to handle all existing future traffic for their region. However, the introduction of a new technology radically dropped the price of fibre, which hampered the expansion plans of many of these telecommunications companies.
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) reduced the demand for fibre by boosting the capacity of a single fibre by a factor of up to 100, which resulted in the plummeting cost of fibre. Across the USA, many telecommunications companies filed for bankruptcy protection as a result of the drop in wholesale price for data communications. But out of the misfortune of one market sector came the good fortune of another. The resulting overcapacity of fibre optic created a new telelcommunications industry; dark fibre.
During the 1990s major exchange carriers would not sell dark fibre to users, thinking that this would cannibalize their lucrative data services. After the dot-com crash, with enormous oversupply of fibre, the marketing for dark fibre became a hot topic in business as demand for data and speed increased.
Since dark fibre offers a dedicated connection to the single business owner, it is best suited to businesses that want high capacity and high speed data transfer. A wide range of applications and industries benefit from fibre optics today, including agriculture, renewable energy, financial services, real estate, transportation and logistics, manufacturing and medical research. Fibre optics is also used for a variety of applications in the military. The need for quick communication in today’s society is evident in every industry.
Yes, UCG can install and maintain dark fibre at your premises. Since 1990, UCG has provided innovative fulfillment solutions for a range of broadband design, cabling & construction projects across New Zealand. Talk to one of our team today to find out more about dark fibre, air blown fibre or HFC networks in your area.
There are several factors that influence the greatest distance that black fibre can travel, including signal attenuation and switch optical design. Typical dark fibre links would be 20km or less, however it is possible to achieve distances of up to 80km for 10 GbE traffic and 40km for 8 GB fibre channel traffic in some specific instances. These sorts of links must be constructed to fulfill extremely high performance criteria and require specialist optics to achieve these distances. Dark fibre is currently capable of supporting bandwidths of up to 100Gbps.
Dark fibre cables are sometimes used in pairs, depending on the equipment port being used. A
Simples port requires a fibre for each direction (i.e. two fibres for a link), and a duplex port allows
transmission in both directions on the same fibre (i.e. a single fibre for a link).
Fibre cables are extremely diverse in terms of the type of fibre used, the way they are constructed and the materials used, as well as the number of fibres present. Optical fibres are exceedingly thin strands of silica (glass) of exceptionally high purity that transfer light from one end to the other with the least amount of loss possible.
Multimode fibre and singlemode fibre are the two most common forms of fibre.
Multiple light rays (modes) can be carried at the same time using multimode fibre, which has variable optical characteristics at its core; simply, light traveling the shortest path (down the middle) travels the slowest.
The bigger core simplifies connections and allows for the use of lower-cost LED and VCSEL technologies that operate in the 850nm wavelength window to be utilised. Because of dispersion, the range is limited, and it is typically utilised as premises and data centre cabling when the distance is less than a kilometre. It is available in two core sizes: 62.5 microns and 50 microns.
Singlemode fibre has a much lower core size of 9 microns and a single light channel, allowing it to traverse much longer distances of up to 100 kilometres. It is also much more cost effective than multimode fibre. These require more expensive electronics that work in multiple wavelength windows and are frequently utilised in long-distance LANs, cable TV, and telephony applications, among other things.